DragonNet
Reference: Claudia Shi et al, Adapting Neural Networks for the Estimation of Treatment Effects, NeurIPS 2019
Implementation remarks: our implementation is exactly the same of
the original paper with the exception of a
sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler which was originally used to
scale predictions.
DragonNet on IHDP
from causalforge.model import Model , PROBLEM_TYPE
from causalforge.data_loader import DataLoader
# load IHDP dataset
r = DataLoader.get_loader('IHDP').load()
X_tr, T_tr, YF_tr, YCF_tr, mu_0_tr, mu_1_tr, X_te, T_te, YF_te, YCF_te, mu_0_te, mu_1_te = r
# model
params={}
params['input_dim'] = X_tr.shape[1]
dragonnet = Model.create_model("dragonnet",
params,
problem_type=PROBLEM_TYPE.CAUSAL_TREATMENT_EFFECT_ESTIMATION,
multiple_treatments=False)
dragonnet.model.summary()
2023-05-08 11:27:39.405731: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:193] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
Model: "model"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input (InputLayer) [(None, 25)] 0 []
dense (Dense) (None, 200) 5200 ['input[0][0]']
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 200) 40200 ['dense[0][0]']
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 200) 40200 ['dense_1[0][0]']
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 100) 20100 ['dense_2[0][0]']
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 100) 20100 ['dense_2[0][0]']
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 100) 10100 ['dense_4[0][0]']
dense_7 (Dense) (None, 100) 10100 ['dense_5[0][0]']
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 201 ['dense_2[0][0]']
y0_predictions (Dense) (None, 1) 101 ['dense_6[0][0]']
y1_predictions (Dense) (None, 1) 101 ['dense_7[0][0]']
epsilon_layer (EpsilonLayer) (None, 1) 1 ['dense_3[0][0]']
concatenate (Concatenate) (None, 4) 0 ['y0_predictions[0][0]',
'y1_predictions[0][0]',
'dense_3[0][0]',
'epsilon_layer[0][0]']
==================================================================================================
Total params: 146,404
Trainable params: 146,404
Non-trainable params: 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Parameters
input_dim: number of inputs
neurons_per_layer: number of neurons per layer (by default,
200)reg_l2: L2 regularization (by default,
0.01)targeted_reg: to use the targeted regularization term (by default,
True)verbose: verbose (by default,
True)val_split: validation split ratio (by default,
0.22)batch_size: batch size (by default,
64)ratio: relative importance of the targeted regularization term, if adopted (by default,
1.0)epochs: number of epochs (by default,
500)learning_rate: learning rate (by default,
1e-5)momentum: momentum (by default,
0.9)use_adam: to use Adam before SGD (by default,
True)adam_epochs: number of epochs to use for Adam, if adopted (by default,
30)adam_learning_rate: learning rate for Adam, if adopted (by default,
1e-3)
Training
from causalforge.metrics import eps_ATE_diff, PEHE_with_ite
import numpy as np
experiment_ids = [1,10,400]
eps_ATE_tr, eps_ATE_te = [], []
eps_PEHE_tr, eps_PEHE_te = [] , []
for idx in experiment_ids:
t_tr, y_tr, x_tr, mu0tr, mu1tr = T_tr[:,idx] , YF_tr[:,idx], X_tr[:,:,idx], mu_0_tr[:,idx], mu_1_tr[:,idx]
t_te, y_te, x_te, mu0te, mu1te = T_te[:,idx] , YF_te[:,idx], X_te[:,:,idx], mu_0_te[:,idx], mu_1_te[:,idx]
# Train your causal method on train-set ...
dragonnet.fit(x_tr,t_tr,y_tr)
# Validate your method test-set ...
ATE_truth_tr = (mu1tr - mu0tr).mean()
ATE_truth_te = (mu1te - mu0te).mean()
ITE_truth_tr = (mu1tr - mu0tr)
ITE_truth_te = (mu1te - mu0te)
eps_ATE_tr.append( eps_ATE_diff( dragonnet.predict_ate(x_tr,t_tr,y_tr), ATE_truth_tr) )
eps_ATE_te.append( eps_ATE_diff( dragonnet.predict_ate(x_te,t_te,y_te), ATE_truth_te) )
eps_PEHE_tr.append( PEHE_with_ite( dragonnet.predict_ite(x_tr), ITE_truth_tr, sqrt=True))
eps_PEHE_te.append( PEHE_with_ite( dragonnet.predict_ite(x_te), ITE_truth_te , sqrt=True))
Epoch 1/30
9/9 [==============================] - 2s 45ms/step - loss: 1933.4249 - regression_loss: 889.4026 - binary_classification_loss: 40.9478 - treatment_accuracy: 0.5728 - track_epsilon: 0.0388 - val_loss: 867.6917 - val_regression_loss: 296.2574 - val_binary_classification_loss: 29.3260 - val_treatment_accuracy: 0.8006 - val_track_epsilon: 0.0409 - lr: 0.0010
Epoch 2/30
9/9 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 475.6049 - regression_loss: 207.7449 - binary_classification_loss: 35.2396 - treatment_accuracy: 0.8106 - track_epsilon: 0.0398 - val_loss: 456.4780 - val_regression_loss: 154.8738 - val_binary_classification_loss: 22.1945 - val_treatment_accuracy: 0.8006 - val_track_epsilon: 0.0395 - lr: 0.0010
...
9/9 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 146.2634 - regression_loss: 54.4143 - binary_classification_loss: 26.8517 - treatment_accuracy: 0.7856 - track_epsilon: 0.0155 - val_loss: 208.7841 - val_regression_loss: 104.0300 - val_binary_classification_loss: 17.8242 - val_treatment_accuracy: 0.9115 - val_track_epsilon: 0.0155 - lr: 1.5625e-07
Epoch 91/100
9/9 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 147.0557 - regression_loss: 54.3474 - binary_classification_loss: 26.8511 - treatment_accuracy: 0.8019 - track_epsilon: 0.0154 - val_loss: 208.5912 - val_regression_loss: 103.8927 - val_binary_classification_loss: 17.8261 - val_treatment_accuracy: 0.9115 - val_track_epsilon: 0.0154 - lr: 1.5625e-07
21/21 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step
3/3 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step
21/21 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step
3/3 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step
Results
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame([[np.mean(eps_ATE_tr),np.mean(eps_ATE_te),np.mean(eps_PEHE_tr),np.mean(eps_PEHE_te)]],
columns=['eps_ATE_tr','eps_ATE_te','eps_PEHE_tr','eps_PEHE_te'],
index=['DragonNet'])
| eps_ATE_tr | eps_ATE_te | eps_PEHE_tr | eps_PEHE_te | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DragonNet | 0.083165 | 0.096781 | 0.668761 | 0.630287 |
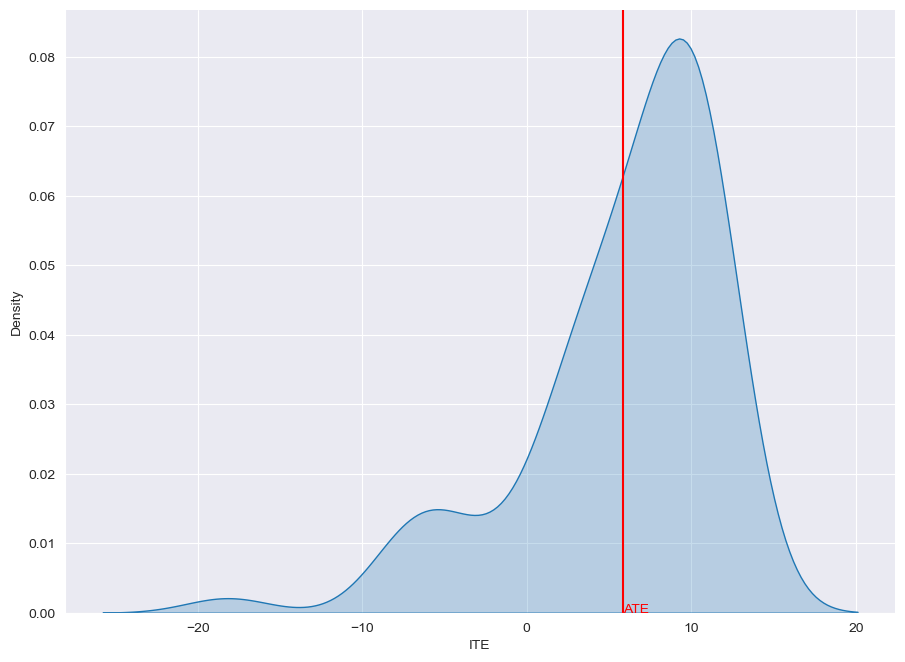
ITE distribution: learned vs. ground truth
Learned
from causalforge.utils import plot_ite_distribution
plot_ite_distribution(dragonnet.predict_ite(x_te))
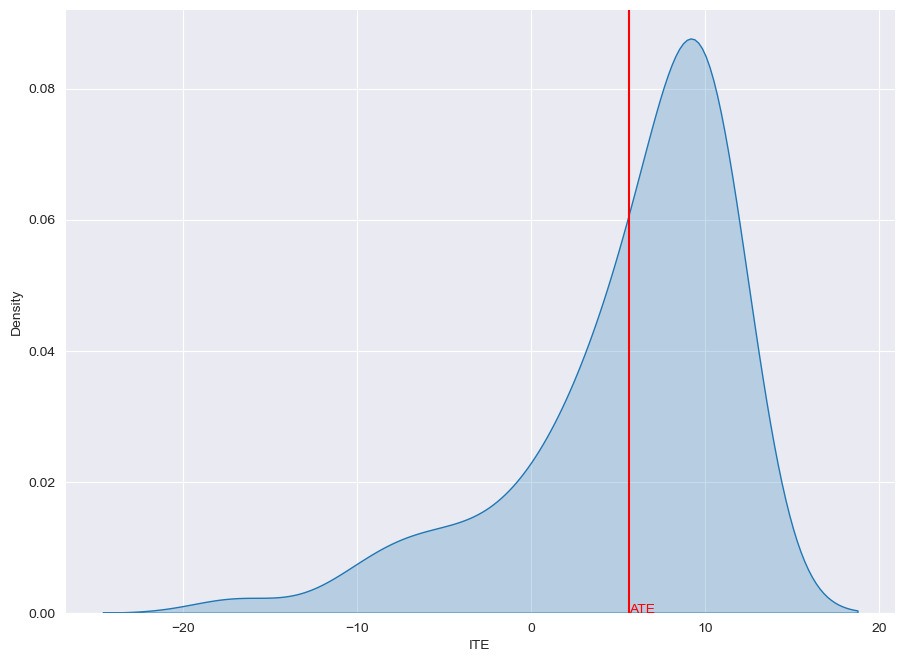
Ground Truth
from causalforge.utils import plot_ite_distribution
plot_ite_distribution(ITE_truth_te)